E-kitaplarda matematik dizgisi¶
Calibre E-kitap görüntüleyicisi e-kitaplara (EPUB ve HTML dosyaları) gömülü matematiği görüntüleme yeteneğine sahiptir. Matematiği doğrudan TeX veya MathML veya AsciiMath ile dizebilirsiniz. Calibre E-kitap görüntüleyici bunu yapmak için mükemmel MathJax kütüphanesini kullanır. Bu, calibre E-kitap görüntüleyiciyle iyi çalışan, içinde matematik bulunan e-kitaplar oluşturmaya ilişkin kısa bir eğitimdir.
Matematik ifadeleri ile basit bir HTML dosyası¶
Basit bir HTML dosyasının içine satır içi matematik yazabilirsiniz ve calibre E-kitap görüntüleyici bunu düzgün dizilmiş matematik haline getirecektir. Aşağıdaki örnekte matematik için TeX gösterimini kullanıyoruz. Ve işaretlerinin ve küçüktür ve büyüktür işaretlerinin sırasıyla & < ve > olarak yazılması gerektiğine dair küçük bir uyarı ile normal TeX komutlarını kullanabileceğinizi göreceksiniz.
The first step is to tell calibre that this will contain mathematics. You do this by adding the following snippet of code to the <head> section of the HTML file:
<script type="text/x-mathjax-config"></script>
That’s it, now you can type mathematics just as you would in a .tex file. For example, here are the Lorenz equations:
<h2>The Lorenz Equations</h2>
<p>
\begin{align}
\dot{x} & = \sigma(y-x) \\
\dot{y} & = \rho x - y - xz \\
\dot{z} & = -\beta z + xy
\end{align}
</p>
Bu parça calibre E-kitap görüntüleyicide aşağıdaki ekran görüntüsüne benziyor.
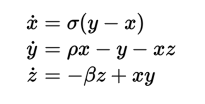
Lorentz Denklemleri¶
Daha fazla denklem ve satır içi matematik içeren eksiksiz HTML dosyası aşağıda yeniden üretilmiştir. Başkalarına kolayca dağıtabileceğiniz bir e-kitap elde etmek için bu HTML dosyasını calibre’de EPUB’a dönüştürebilirsiniz.
Oluşturulmuş EPUB dosyası: mathjax.epub.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<!-- Copyright (c) 2012 Design Science, Inc. -->
<head>
<title>Math Test Page</title>
<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" />
<!-- This script tag is needed to make calibre's ebook-viewer recpgnize that this file needs math typesetting -->
<script type="text/x-mathjax-config">
// This line adds numbers to all equations automatically, unless explicitly suppressed.
MathJax.tex = {tags: 'all'};
</script>
<style>
h1 {text-align:center}
h2 {
font-weight: bold;
background-color: #DDDDDD;
padding: .2em .5em;
margin-top: 1.5em;
border-top: 3px solid #666666;
border-bottom: 2px solid #999999;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Sample Equations</h1>
<h2>The Lorenz Equations</h2>
<p>
\begin{align}
\dot{x} & = \sigma(y-x) \label{lorenz}\\
\dot{y} & = \rho x - y - xz \\
\dot{z} & = -\beta z + xy
\end{align}
</p>
<h2>The Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality</h2>
<p>\[
\left( \sum_{k=1}^n a_k b_k \right)^{\!\!2} \leq
\left( \sum_{k=1}^n a_k^2 \right) \left( \sum_{k=1}^n b_k^2 \right)
\]</p>
<h2>A Cross Product Formula</h2>
<p>\[
\mathbf{V}_1 \times \mathbf{V}_2 =
\begin{vmatrix}
\mathbf{i} & \mathbf{j} & \mathbf{k} \\
\frac{\partial X}{\partial u} & \frac{\partial Y}{\partial u} & 0 \\
\frac{\partial X}{\partial v} & \frac{\partial Y}{\partial v} & 0 \\
\end{vmatrix}
\]</p>
<h2>The probability of getting \(k\) heads when flipping \(n\) coins is:</h2>
<p>\[P(E) = {n \choose k} p^k (1-p)^{ n-k} \]</p>
<h2>An Identity of Ramanujan</h2>
<p>\[
\frac{1}{(\sqrt{\phi \sqrt{5}}-\phi) e^{\frac25 \pi}} =
1+\frac{e^{-2\pi}} {1+\frac{e^{-4\pi}} {1+\frac{e^{-6\pi}}
{1+\frac{e^{-8\pi}} {1+\ldots} } } }
\]</p>
<h2>A Rogers-Ramanujan Identity</h2>
<p>\[
1 + \frac{q^2}{(1-q)}+\frac{q^6}{(1-q)(1-q^2)}+\cdots =
\prod_{j=0}^{\infty}\frac{1}{(1-q^{5j+2})(1-q^{5j+3})},
\quad\quad \text{for $|q|<1$}.
\]</p>
<h2>Maxwell's Equations</h2>
<p>
\begin{align}
\nabla \times \vec{\mathbf{B}} -\, \frac1c\, \frac{\partial\vec{\mathbf{E}}}{\partial t} & = \frac{4\pi}{c}\vec{\mathbf{j}} \\
\nabla \cdot \vec{\mathbf{E}} & = 4 \pi \rho \\
\nabla \times \vec{\mathbf{E}}\, +\, \frac1c\, \frac{\partial\vec{\mathbf{B}}}{\partial t} & = \vec{\mathbf{0}} \\
\nabla \cdot \vec{\mathbf{B}} & = 0
\end{align}
</p>
<h2>Inline Mathematics</h2>
<p>While display equations look good for a page of samples, the
ability to mix math and text in a paragraph is also important. This
expression \(\sqrt{3x-1}+(1+x)^2\) is an example of an inline equation. As
you see, equations can be used this way as well, without unduly
disturbing the spacing between lines.</p>
<h2>References to equations</h2>
<p>Here is a reference to the Lorenz Equations (\ref{lorenz}). Clicking on the equation number will take you back to the equation.</p>
</body>
</html>
Not
The calibre E-book viewer supports MathML as well as TeX, but you must
include the <script type="text/x-mathjax-config"></script> line in
your HTML file otherwise the MathML will not render.
Daha fazla bilgi¶
Calibre E-kitap görüntüleyici matematiği işlemek için MathJax kütüphanesini kullandığından, e-kitaplarda matematik hakkında daha fazla bilgi edinmek ve yardım almak için en iyi yer MathJax web sitesi’dur.