Typesetting mathematics in e-books¶
The calibre E-book viewer has the ability to display mathematics embedded in e-books (EPUB and HTML files). You can typeset the mathematics directly with TeX or MathML or AsciiMath. The calibre E-book viewer uses the excellent MathJax library to do this. This is a brief tutorial on creating e-books with mathematics in them that work well with the calibre E-book viewer.
Eine einfache HTML-Datei mit Formeln¶
You can write mathematics inline inside a simple HTML file and the calibre E-book viewer will render it into properly typeset mathematics. In the example below, we use TeX notation for mathematics. You will see that you can use normal TeX commands, with the small caveat that ampersands and less than and greater than signs have to be written as & < and > respectively.
The first step is to tell calibre that this will contain mathematics. You do this by adding the following snippet of code to the <head> section of the HTML file:
<script type="text/x-mathjax-config"></script>
That’s it, now you can type mathematics just as you would in a .tex file. For example, here are the Lorenz equations:
<h2>The Lorenz Equations</h2>
<p>
\begin{align}
\dot{x} & = \sigma(y-x) \\
\dot{y} & = \rho x - y - xz \\
\dot{z} & = -\beta z + xy
\end{align}
</p>
This snippet looks like the following screen shot in the calibre E-book viewer.
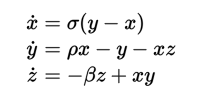
Die Lorentz-Gleichung¶
The complete HTML file, with more equations and inline mathematics is reproduced below. You can convert this HTML file to EPUB in calibre to end up with an e-book you can distribute easily to other people.
Hier ist die generierte EPUB-Datei: mathjax.epub.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<!-- Copyright (c) 2012 Design Science, Inc. -->
<head>
<title>Math Test Page</title>
<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" />
<!-- This script tag is needed to make calibre's ebook-viewer recpgnize that this file needs math typesetting -->
<script type="text/x-mathjax-config">
// This line adds numbers to all equations automatically, unless explicitly suppressed.
MathJax.tex = {tags: 'all'};
</script>
<style>
h1 {text-align:center}
h2 {
font-weight: bold;
background-color: #DDDDDD;
padding: .2em .5em;
margin-top: 1.5em;
border-top: 3px solid #666666;
border-bottom: 2px solid #999999;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Sample Equations</h1>
<h2>The Lorenz Equations</h2>
<p>
\begin{align}
\dot{x} & = \sigma(y-x) \label{lorenz}\\
\dot{y} & = \rho x - y - xz \\
\dot{z} & = -\beta z + xy
\end{align}
</p>
<h2>The Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality</h2>
<p>\[
\left( \sum_{k=1}^n a_k b_k \right)^{\!\!2} \leq
\left( \sum_{k=1}^n a_k^2 \right) \left( \sum_{k=1}^n b_k^2 \right)
\]</p>
<h2>A Cross Product Formula</h2>
<p>\[
\mathbf{V}_1 \times \mathbf{V}_2 =
\begin{vmatrix}
\mathbf{i} & \mathbf{j} & \mathbf{k} \\
\frac{\partial X}{\partial u} & \frac{\partial Y}{\partial u} & 0 \\
\frac{\partial X}{\partial v} & \frac{\partial Y}{\partial v} & 0 \\
\end{vmatrix}
\]</p>
<h2>The probability of getting \(k\) heads when flipping \(n\) coins is:</h2>
<p>\[P(E) = {n \choose k} p^k (1-p)^{ n-k} \]</p>
<h2>An Identity of Ramanujan</h2>
<p>\[
\frac{1}{(\sqrt{\phi \sqrt{5}}-\phi) e^{\frac25 \pi}} =
1+\frac{e^{-2\pi}} {1+\frac{e^{-4\pi}} {1+\frac{e^{-6\pi}}
{1+\frac{e^{-8\pi}} {1+\ldots} } } }
\]</p>
<h2>A Rogers-Ramanujan Identity</h2>
<p>\[
1 + \frac{q^2}{(1-q)}+\frac{q^6}{(1-q)(1-q^2)}+\cdots =
\prod_{j=0}^{\infty}\frac{1}{(1-q^{5j+2})(1-q^{5j+3})},
\quad\quad \text{for $|q|<1$}.
\]</p>
<h2>Maxwell's Equations</h2>
<p>
\begin{align}
\nabla \times \vec{\mathbf{B}} -\, \frac1c\, \frac{\partial\vec{\mathbf{E}}}{\partial t} & = \frac{4\pi}{c}\vec{\mathbf{j}} \\
\nabla \cdot \vec{\mathbf{E}} & = 4 \pi \rho \\
\nabla \times \vec{\mathbf{E}}\, +\, \frac1c\, \frac{\partial\vec{\mathbf{B}}}{\partial t} & = \vec{\mathbf{0}} \\
\nabla \cdot \vec{\mathbf{B}} & = 0
\end{align}
</p>
<h2>Inline Mathematics</h2>
<p>While display equations look good for a page of samples, the
ability to mix math and text in a paragraph is also important. This
expression \(\sqrt{3x-1}+(1+x)^2\) is an example of an inline equation. As
you see, equations can be used this way as well, without unduly
disturbing the spacing between lines.</p>
<h2>References to equations</h2>
<p>Here is a reference to the Lorenz Equations (\ref{lorenz}). Clicking on the equation number will take you back to the equation.</p>
</body>
</html>
Bemerkung
The calibre E-book viewer supports MathML as well as TeX, but you must
include the <script type="text/x-mathjax-config"></script> line in
your HTML file otherwise the MathML will not render.
Weitere Informationen¶
Since the calibre E-book viewer uses the MathJax library to render mathematics, the best place to find out more about mathematics in e-books and get help is the MathJax website.